In the article we will try to reveal the main principles of the car clutch operation, the components and which types distinguish them. In the article we will try to reveal the main principles of the car clutch operation, the components and which types distinguish them.

A sharp start from a standstill, or a heavy load while driving quickly removes the clutch from the working state, the first sign of a clutch breakdown is poor gear shifting, slipping after switching on the gear, pressing the gas, the engine speed rose, and the car does not pick up speed. All this leads to one thing, it's time to change the clutch. But nevertheless, it is not a problem to replace, but in order to prevent such a misfortune from happening again, we will consider the principle of the clutch.
What is clutch?

The clutch (or as it is also called the "friction clutch") is the mechanism of a car that connects the engine to the transmission and from time to time makes it possible to disconnect them when changing gear, braking or during a stop. The main task of the clutch is the frictional interaction of the discs, which are located on both shafts.
Another function of the clutch is the ability to smoothly move the car from a standstill. Since the engine shaft rotates, and the transmission shaft is in a fixed stationary position, it is impossible to start the movement of the machine without a clutch, since it helps the shafts to smoothly rub against each other, and at the same time provides a smooth acceleration of revolutions that the shafts provide, and finally - then drive the vehicle.
If, by chance (or not by chance), too quickly and abruptly disconnect those two shafts, then the stationary transmission shaft will jam the rotating engine shaft and your car will simply stall (at best), or there will be breakdowns in the clutch mechanism that will require considerable material costs. Basically, mechanical clutches are installed on modern cars.
What the clutch consists of

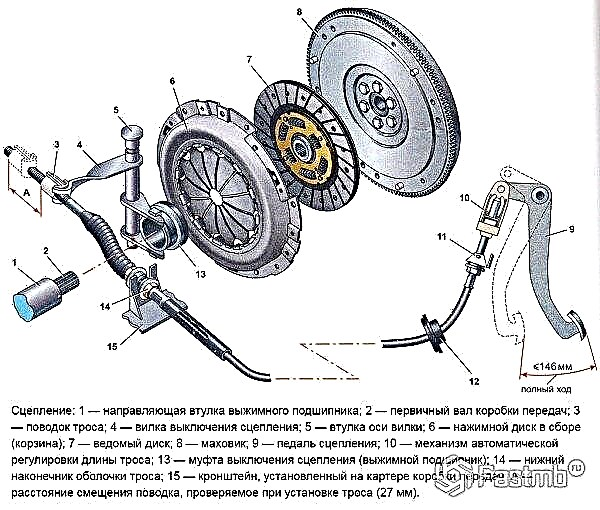
In order not to break the clutch, you need to know not only how it works superficially and what its functions, but also what parts it consists of. The main constituent parts include the driven and driving parts, the shut-off mechanism and the pressure system.
The engine torque is transmitted from the flywheel to the drive part, the latter, in turn, transmit torque to the gearbox drive shaft. The frictional moment is provided by the push mechanism, which, thanks to the tight adhesion of the driven and driving parts, gives the long-awaited result of movement.
Disengaging the clutch is considered important. So one disc, on which the springs are peripherally located, is located in a cast iron crankcase, which, in turn, is located in the engine block crankcase. The leading part includes the clutch cover and flywheel, the latter, in turn, is attached to the crankshaft flywheel by means of six special bolts ... The pressure plate is located in the middle of the casing. The torque of the pressure plate is transmitted from the flywheel through three protrusions that are contained in the disc and enter the housing windows. The driven disc, the hub, the drive shaft of the gearbox are the main and mandatory components of the driven part of the clutch.
On both sides of the driven disc there are friction linings made of copper-asbestos composition (or other metal-asbestos composition), which withstand unusually high temperatures and are known for their frictional properties. The driven disc is connected to the hub by rivets or through springs. These springs are an integral part of a spring-friction damper for rotating vibrations (that is, a damper).
Mechanical clutch

By depressing the clutch pedal, we know that we need to change gear, but how the principle works inside the basket, few people know. At this time, the driven disc is clamped between the flywheel and the pressure plate. When the hitch pedal is depressed, the drive cable is displaced in the basket and at the same time the lever is rotated, which is responsible for the fastening. At the same time, the free end of the fork starts to press against the release bearing. He, in turn, moving to the basket, presses on the discs. After this maneuver, the discs begin to move the pressure plate.
At the same moment, the driven disc is unloaded from the force with which this driven disc is pressed against the basket (aka the flywheel). In the given sequence, the clutch is disengaged. It is after this that the driver of the car can freely change gear. By smoothly releasing the clutch pedal, the driver connects the driven disc to the basket. As a result of such manipulations, the rotating moment is transmitted to the chassis and the car is brought into driving mode.
As you can see, all efforts are transmitted through mechanical components, there are no auxiliary elements.
Hydraulic clutch

Judging by the name of this type of clutch, I think that it has become clear to you that in a hydraulic drive all efforts, from the clutch pedal to the mechanism itself, are transported with the help of such a fluid. It, in turn, is located in hydraulic cylinders and tubes that connect all the elements necessary in the mechanism. The structure of the hydraulic clutch is not very similar to the mechanical clutch.
One disc, large enough, sits on the sharp end of the drive shaft and steel casing. The cover is attached to the flywheel. There is a spring with radial petals inside the casing. They are, say, release levers. A control pedal is located on the axis. It is also raised to the body, namely to the bracket. The main cylinder pusher is attached to the clutch pedal with the assistance of a hinge. The pedal is released when the clutch is disengaged and the gear is shifted.
Clutch diagnostics at home

The photo shows the clutch elements of the Lada Priora car
Most often, when a breakdown occurs, characteristic sounds are heard. To do this, press the clutch pedal a couple of times and listen carefully. If extraneous sounds appear, for example, such as creaking, knocking or the like, then it is worth understanding where they are coming from and eliminating them. When you press the pedal, it should go freely, without jerks and delays. The distance from the floor to the pedal when turned on or off should not exceed 145 millimeters.
- Read an article about adjusting the clutch drive on a VAZ 2110 car
There are also breakdowns while driving, namely when you change gear. If it's hard to turn on the gear and when you turn it on, a non-standard crunch, noise and other sounds appear, then you should not delay it. Also, when you turn on the gear and press the gas, the car is not as fast as usual, it begins to smoothly pick up speed, while the engine runs at maximum. This is the first sign of a broken clutch disc.
- Read about clutch repair on a VAZ car